For a Continuous and Oriented Fiber reinforced Composite
Fiber-reinforced composites are composed of axial particulates embedded in a matrix material . The objective of fiber-reinforced composites it to obtain a material with high specific strength and high specific modulus. (i.e. high strength and high elastic modulus for its weight.) The strength is obtained by having the applied load transmitted from the matrix to the fibers. Hence, interfacial bonding is important.
Classic examples of fiber-reinforced composites include fiberglass and wood.
Fiber Geometry
Some common geometries for fiber-reinforced composites:
- Aligned
The properties of aligned fiber-reinforced composite materials are highly anisotropic. The longitudinal tensile strength will be high whereas the transverse tensile strength can be much less than even the matrix tensile strength. It will depend on the properties of the fibers and the matrix, the interfacial bond between them, and the presence of voids.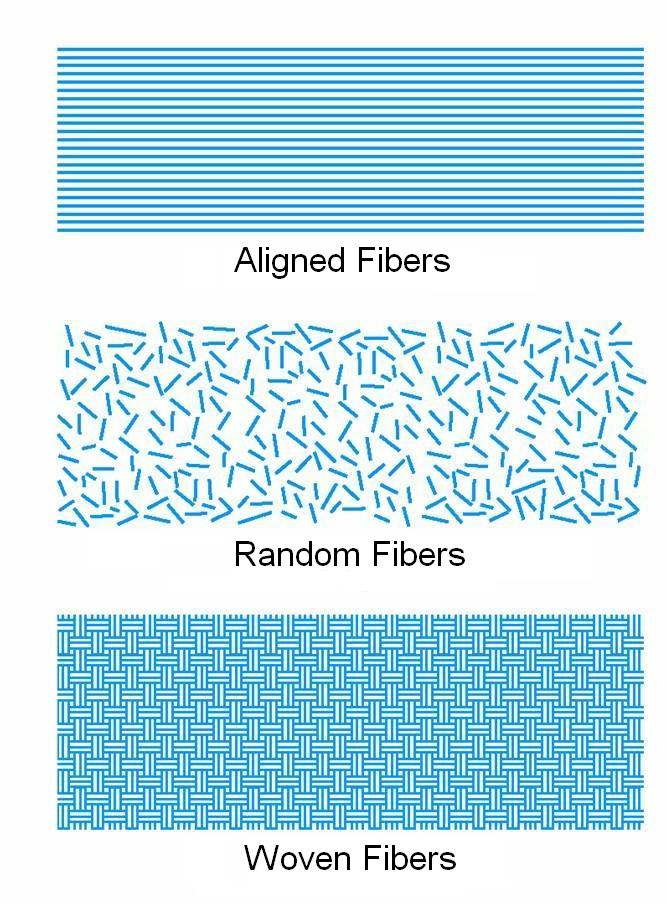
There are 2 different geometries for aligned fibers:
- Continuous & Aligned
The fibers are longer than a critical length whichis the minimum length necessary such that the entire load is transmitted from the matrix to the fibers. If they are shorter than this critical length, only some of the load is transmitted. Fiber lengths greater that 15 times the critical length are considered optimal. Aligned and continuous fibers give the most effective strengthening for fiber composites.
- Discontinuous & Aligned
The fibers are shorter than the critical length. Hence discontinuous fibers are less effective in strengthening the material, however, their composite modulus and tensile strengths can approach 50-90% of their continuous and aligned counterparts. And they are cheaper, faster and easier to fabricate into complicated shapes. - Random
This is also called discrete, (or chopped) fibers . T he strength will not be as high as with aligned fibers, however, the advantage is that the material will be istropic and cheaper.
- Woven
The fibers are woven into a fabric which is layered with the matrix material to make a laminated structure .
Fiber Cross Section
Of course, the fiber cross sectional shape and size is also important.
Here are some examples of the cross-sectional areas and shapes for a wide variety of reinforing fibers: Whiskers
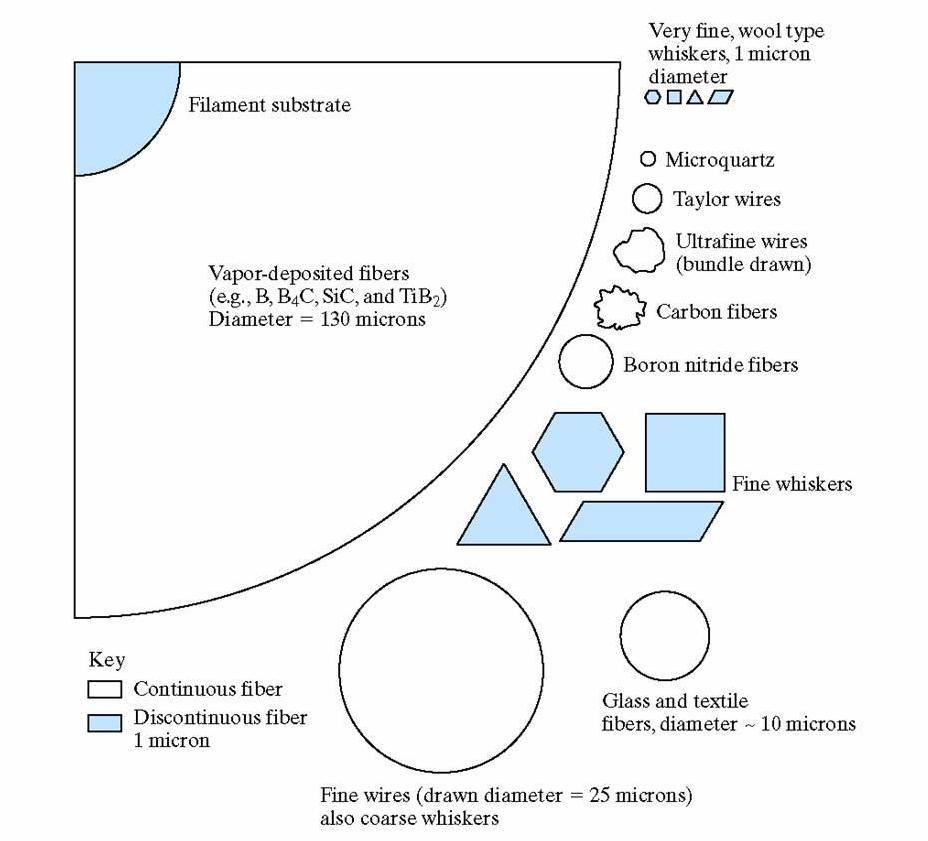 Some general catagories of fibers based on cross section:
Some general catagories of fibers based on cross section:
- very small diameter (~1 micron) single crystals
- strong because they are virtually flaw free
- expensive
- difficult to put in a matrix
- examples include graphite (C), SiN, Al2O3, SiC
- small diameters (~10 microns)
- can be polycrystalline or amorp hous
- large diameters (~25 microns)
- made from metals such as steel, Mo, W
Fiber Materials for Fiberglass
And of course, the fiber material is important too.
A commonly used glass fiber composition for structural composites is E-glass, in which E stands for "electrical type". It is a lime-aluminum-borosilicate glass with zero or low sodium and potassium levels. It is popular because it has chemical durability. A more advanced and expensive fiber is S-glass, a magnesia-alumina-silicate glass that is used for high-strength applications.
The composition of these and other common glass fiber materials are listed here:
| Designation | Characteristic | Composition | ||||||||
| SiO2 | Al2O3 + Fe2O3 | CaO | MgO | Na2O | K2O | B2O3 | TiO2 | ZrO2 | ||
| A-glass | common soda-lime silica | 72 | <1 | 10 | 14 | |||||
| AR-glass | alkali resistnat (for concrete reinforcement) | 61 | <1 | 5 | <1 | 14 | 3 | 7 | 10 | |
| C-glass | chemical corrosion resistant | 65 | 4 | 13 | 3 | 8 | 2 | 5 | ||
| E-glass | electrical composition | 54 | 15 | 17 | 5 | <1 | <1 | 8 | ||
| S-glass | high strength and modulus | 65 | 25 | 10 | ||||||
Some common thermosetting polymeric matrix materials for fiberglass include epoxies, polyesters, phenolics and silicones. Some of the common thermoplastic polymer ic matrix materials for fiberglass include nylon 66, polycarbonate and polystyrene. Advanced Fiber-Reinforced Composite Systems Other Than Fiberglass
Advanced composites include those systems in which reinforcing fibers have moduli higher than that of E-glass.
Here is a list of a variety of advanced composite systems.
| Class | Fiber | Matrix |
| Polymer matrix | Para-aramid (Kevlar)1 | epoxy |
| Para-aramid (Kevlar) | polyester | |
| C (graphite)2 | epoxy | |
| C (graphite) | polyester | |
| C (graphite) | polyetheretherketone (PEEK) | |
| C (graphite) | polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) | |
| Metal matrix | B | Al |
| C | Al | |
| Al2O3 | Al | |
| Al2O3 | Mg | |
| SiC | Al | |
| SiC | Ti (alloys) | |
| Ceramic matrix | Nb | MoSi2 |
| C | C | |
| C | SiC | |
| SiC | Al2O3 | |
| SiC | SiC | |
| SiC | Si3N4 | |
| SiC | Li-Al-silicate (glass-ceramic) |
- Kevlar is a Du Pont trade name for poly p-phenyleneterephthalamide (PPD-T). It is an aramid, i.e. an aromatic (benzene ring type) polyamide polymer fiber with a very rigid m olecular structure. It is used for high-performance composite applications where light weight, high strength and stiffness, damage resistance, and resistance to fatigue, creep, and stress rupture are important.
- Kevlar 29 is a low-density high-strength aramid fiber designed for such applications as ballistic protection, ropes, and cables.
- Kevlar 49 is characterized by a low density and high strength and modulus. It is used as reinforcement for plastics in composites for aerospace, marine, automotive, and other industrial applications.
- Carbon fibers are made of graphitic and noncrystalline regions. It has the highest specific strength and specific modulus of all fiber materials. It retains tensile strength at high temperatures and is not affected by moisture, solvents, acids or bases at room temperatures. However, at high temperatures it is subject to oxidation.
PREVIOUS PAGE NEXT PAGE
Source: https://fog.ccsf.edu/~wkaufmyn/ENGN45/Course%20Handouts/14_CompositeMaterials/03_Fiber-reinforcedComposites.html
0 Response to "For a Continuous and Oriented Fiber reinforced Composite"
Post a Comment